Education
What is CBD?
CBD is cannabidiol, a natural compound found in flowers and leaves of hemp plants. It contains a variety of cannabinoids and terpenes which interact with the human endocannabinoid system (ECS).
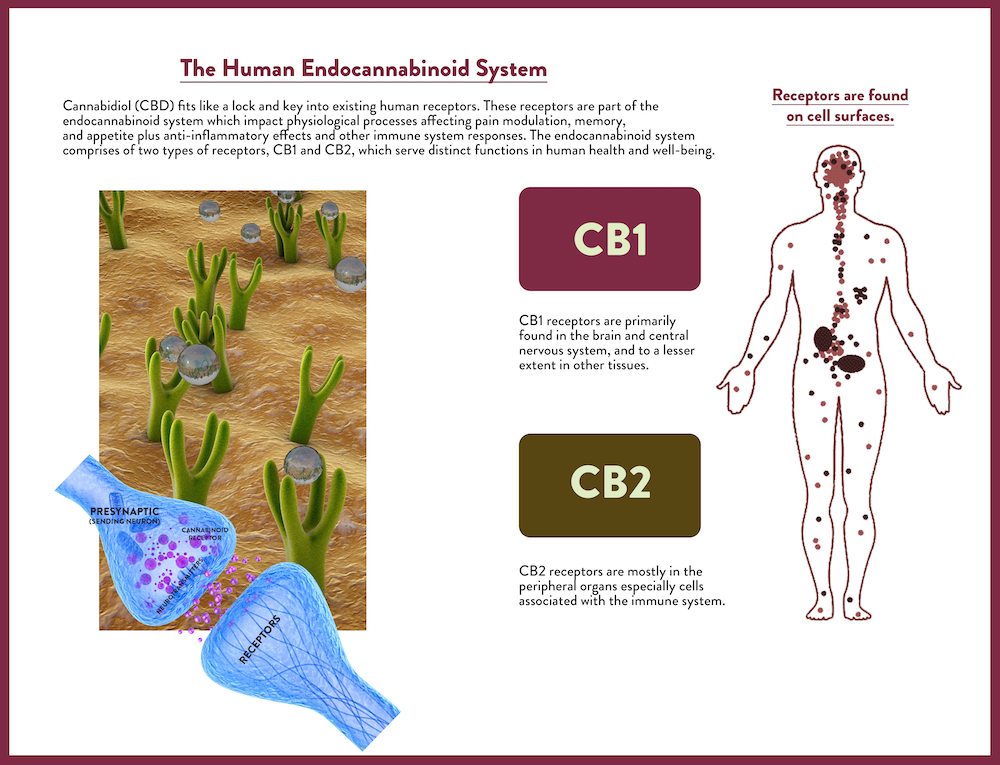
The Endocannabinoid System
Humans (and some furry friends!) have an Endocannabinoid System (ECS) in their bodies. This system is comprised of a series of receptors throughout the body which serve most major systems, including the organs and the central nervous system.
What are Cannabinoids?
Cannabinoids are produced by all cannabis plants and are active compounds which account for most of the benefits of cannabis. Technically these are called "phytocannabinoids". All mammals bodies produce Endocannabinoids on their own, while phytocannabinoids are derived from plants and closely mimic endocannabinoids.
There are other compounds from the hemp plant which are similar to CBD, but for the sake of this educational piece, we will focus on CBD.

Endocannabinoids are technically called neurotransmitters and are produced by the body in response to varying states of health and environmental situations. They interact with the many receptors throughout the body. Neurotransmitter's jobs are to signal the cell or cells to adjust what it's doing or how it's reacting to other neurotransmitters. It's like a human superhighway intended to communicate with every corner of the body.
If something in the body is out of balance, the nervous system sends neurotransmitters to interact with the receptors on the cells, with the intention to help rebalance their activities.
Endocannabinoids, therefore, work with the endocannabinoid receptors to regulate different systems, such as sleeping, appetite, moods, immune response, metabolism and more. Click here to learn about CBD and your immune system.